Despite the emergence of other energy sources, coal remains a vital energy source for heating, power, and industrial needs.
The United States, China, Australia and many other countries have significant coal reserves and employ millions of miners worldwide.
Coal mining is an intricate process with a long and rich historical tradition.
⛏️ What Is Coal?
Coal belongs to a class of energy sources called "fossil fuels."
They get their name from how coal deposits started out millions of years ago as the remains of plants and animals trapped deep underground.
Time, pressure, and decay turned the remains into different types of coal deposits with varying industrial uses.
The coal produced by modern mining operations serves many functions, such as:
- use in coal-fired power plants for power generation
- home heating
- manufacture of diesel fuel
- agriculture
- steel manufacturing
There are several types of coal. Some are more valuable than others.
Anthracite goes by many names, including "black coal" and "hard coal."
Pennsylvania is a major source of anthracite. Anthracite costs more than the more common forms of coal. Its main advantages are its low sulfur content and ability to burn cleanly.
Bituminous coal is the most common type of coal. It produces black smoke when it burns, but it is relatively inexpensive.
Lignite or "brown coal" has high moisture content and low carbon content. It is less valuable for heat production. However, many people use lignite briquettes for residential heating, and the ash from burning lignite can fertilize crops and plants.
Sub-bituminous coal has a higher carbon content than lignite. It is an energy source for coal-fired power plants.
⛏️ The History of Coal Mining
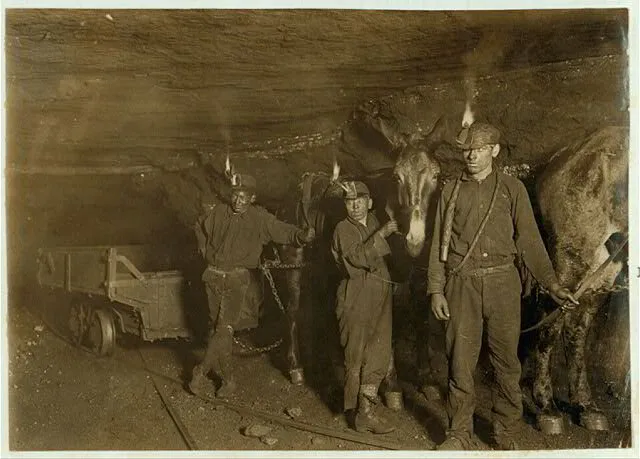
Image Courtesy of Library of Congress, Drivers and Mules, Gary, W. Va., Mine, Where much of the mining and carrying is done by machinery. Location: Gary, West Virginia., 1908.
Civilizations developed the technology for fossil fuel mining technology over thousands of years. In ancient times, burning coal provided heat for baths, forges, and buildings.
Beginning in the 18th century, the Industrial Revolution vastly increased the demand for cheap energy sources. Factories, transportation, and power plants came to depend on coal.
Coal production skyrocketed into the 20th century, dipped during the Depression of the 1930s, and rebounded with the start of World War II.
In the 21st century, coal production has decreased. This decline has led some commentators and politicians to question the long-term future of the coal industry.
⛏️ Methods of Mining Coal
Conventional mining can access coal seams in many ways. The best approach for mining a specific coal deposit depends on the depth, shape, and composition of the deposit.
In most situations, rock and soil cover the coal deposits. This material is the overburden. Companies will often choose a cost-effective type of mining that allows them to get through, around, or under the overburden.
Surface Coal Mining
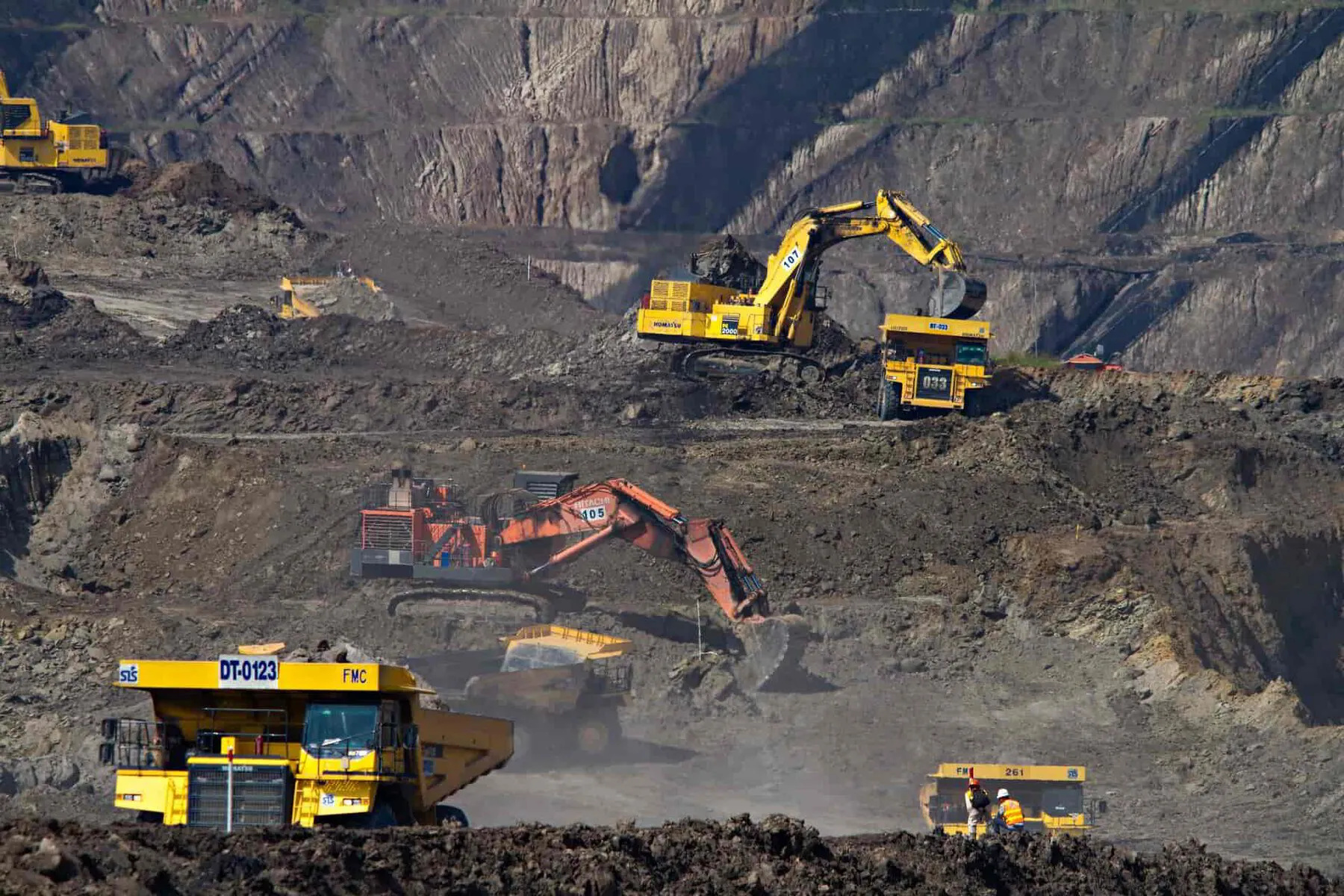
Most of the coal that companies extract today comes from surface mining.
Surface mining has many advantages over other techniques in the tools needed, the safety risks, and the costs of eventual remediation.
Surface mining is only viable if the coal seam is at or very near the surface. In this situation, the miners can extract the coal from the ground and cart it away.
The technique avoids some of the environmental and safety hazards of underground mining.
One common form of surface mining is strip mining. With this method, miners strip away overburden to reveal deposits underneath.
Strip mines can be controversial if the land above the coal deposit is a habitat for animals or essential to the environment.
Mountaintop Removal
If a coal seam exists within a mountain or rock formation, miners can remove the surface layers of the mountain to access the seam without digging tunnels.
Mountaintop removal can give miners access to seams when the steep terrain prevents them from using other mining techniques.
The mountaintop removal strategy has higher remediation costs, which has prompted backlash from environmentalist groups.
Mountaintop removal can endanger nearby streams. Furthermore, restoring the original contour of the mining site is typically expensive and time-consuming.
Underground Coal Mining or Deep Mining
Underground coal mines fall into several types. Each type best corresponds to coal seams of different shapes.
Room-and-pillar mining is a type of underground mining where the miners clear out swaths of underground ore.
As a result, they leave behind underground spaces ("rooms") separated by sections of intact or ("pillars") that support the overhead rock. Therefore, the rock does not collapse on the rooms.
Room-and-pillar mines allow for continuous mining. This process uses robotic equipment to move vast amounts of coal quickly.
Longwall mining mines a single coal seam in one single tunnel, rather than the many rooms used in the room-and-pillar technique.
Contour mining is similar to longwall mining, but it follows the contour of a seam.
⛏️ Tools of Mining
A mining company will need tools for exploration, extraction, and remediation or reclamation at mining sites.
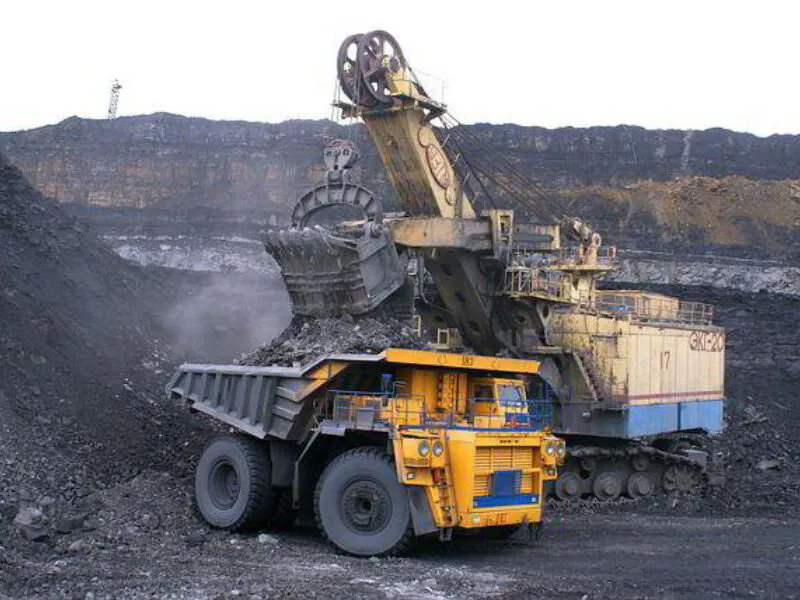
Miners use hydraulic shovels called power shovels to dig out coal, clear debris, and remove rocks in surface and underground mining.
Miners use a range of vehicles such as bulldozers, mining trucks, and loaders.
These vehicles move coal within underground mines, carry coal from the coal bed in surface mines, and transport coal to the coal preparation plant.
Explosives are an indispensable but potentially dangerous tool in the modern miner's arsenal. Miners use explosives to blast tunnels and clear overburden from the top of surface deposits.
⛏️ How Does a Coal Mine Work?
Mining is a highly complex process. It requires long-term planning, a significant investment of time and money, careful execution, and responsible cleanup.
During the exploration stage, companies locate and identify deposits. Due to centuries of concerted mining activity, many of the most accessible coal sources are no longer economically viable.
As mining depletes deposits, it costs more to extract the remaining coal than what the coal is worth.
Mining companies must obtain permits and demonstrate the legal right to mine in a particular way at a certain location before they can start mining operations.
Once permits are in hand, companies move their mining equipment into place, access the coal, and haul it away for processing.
To extract coal from coal beds and seams, miners must move overburden out of the way. This discarded rock is called spoil. Spoil can be harmful to the natural environment.
After coal extraction, the coal goes to the coal preparation plant. There, a washing process removes impurities, and a sorting process breaks up the coal into pieces of different sizes. The pieces then go to market.
In modern mining, laws require coal miners to carry out remediation on the mining site to repair some of the damage from the mining process.
The requirements vary based on the country, state, province, or local jurisdiction that the mining site occupies.
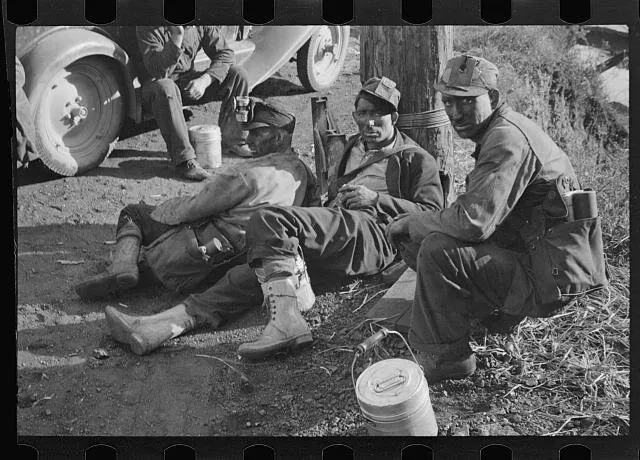
⛏️ Safety Risks of Underground Mining
Image Courtesy of Library of Congress, Group of coal miners, Williamson, West Virginia, 1935.
Like firefighters and loggers, coal miners face the elements on a daily basis. Contemporary mining is safer than in the past, but it still involves risk.
Companies have moral and legal responsibilities to provide miners with safety equipment, ventilation, and a safe way to exit the mine in an emergency.
Exposure to coal particles over a long period can be dangerous. Miners with inadequate protective equipment face the risk of diseases.
The chief of these diseases is "black lung," a chronic lung disease that happens when miners breathe in coal dust.
Toxic gases, called "damp," build up in coal mines, particularly those with underground mining lacking sufficient ventilation.
Nitrogen displaces oxygen in the air, causing suffocation. Carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and methane are toxic.
Water sprays can protect miners from damp by pulling dust and gases out of the air.
Fine dust particles of flammable materials often ignite in the presence of a flame. In the confines of a mine, they can trigger explosions that kill miners.
These explosions may cause death directly from the blast or indirectly by causing a collapse or filling the air with toxic debris.
Miners are also at risk of becoming injured or trapped when a mine tunnel collapses.
In 2010, a collapse in a Chilean mine trapped 33 miners for over two months.
In Indonesia in 2020, 11 workers were killed n a landslide at an illegal coal mining site.
Methane or natural gas deposits often occur near coal. These deposits build up as plant and animal remains decay. Natural gas is odorless, toxic, and flammable.
The term "canary in a coal mine" refers to the old practice of bringing a canary into the tunnels.
Natural gas and carbon dioxide would kill the canary more quickly than the miners, giving them a chance to escape.
⛏️ Environmental Risks of Surface and Underground Mining
Coal mining involves substantial disruption of the land in the vicinity of the coal seam and the risk of releasing pollutants into the air and water.
It can release methane and other toxins into the air. Dirt, rock, coal dust, and other contaminants can mix with rainwater and spill from mined land into nearby waterways.
Natural gas is a greenhouse gas that contributes to global warming. Therefore, modern mines must take precautions to reduce methane emissions and other forms of air pollution.
⛏️ Learning More about Underground Mining
To learn more about coal resources and coal mining techniques, visit An Underground Miner blog on our website.
You can also join our friendly Facebook group and learn from our blog with informative news stories.
This article was written by An Underground Miner